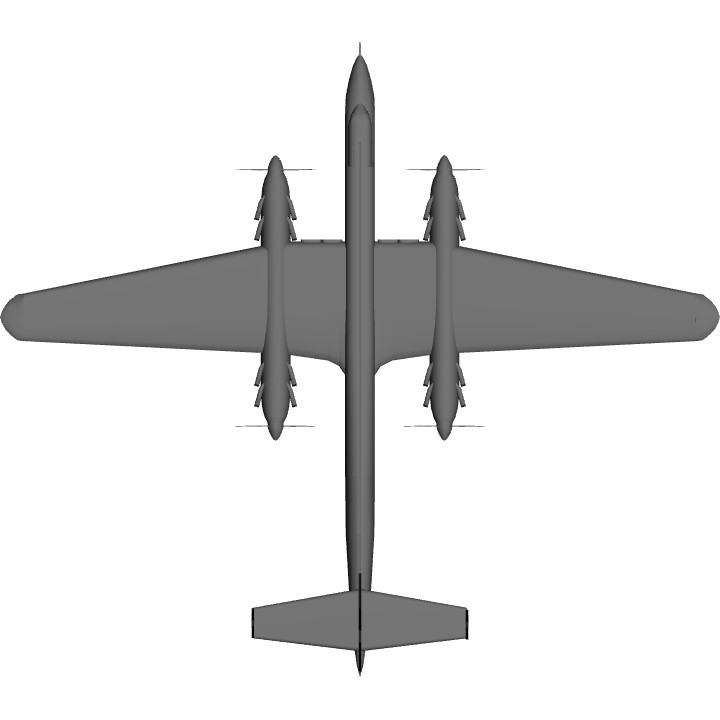
IL-14T - Stalin’s “KV-2 of the Skies”
This is my build to celebrate my entrance into the huge gold club. It’s been hard getting to where I am right now, but I am grateful for all the support, tips, XML assistance, and friends that helped me get where I am now.
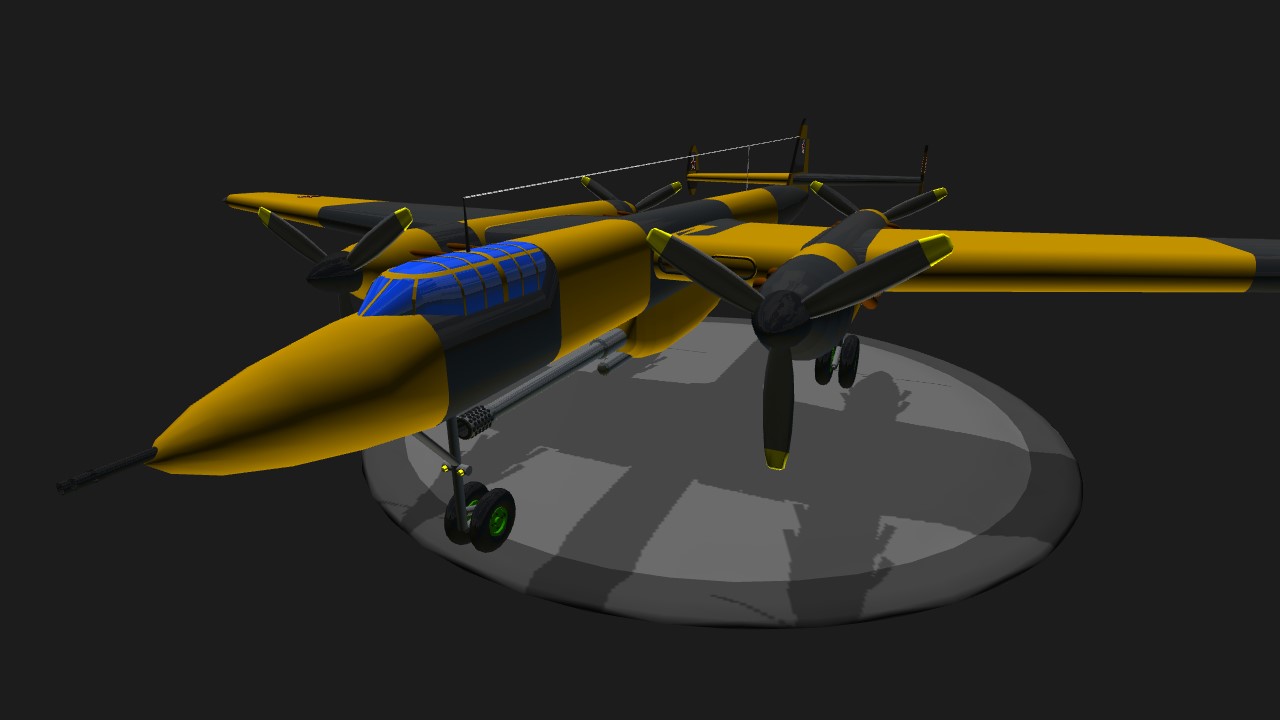
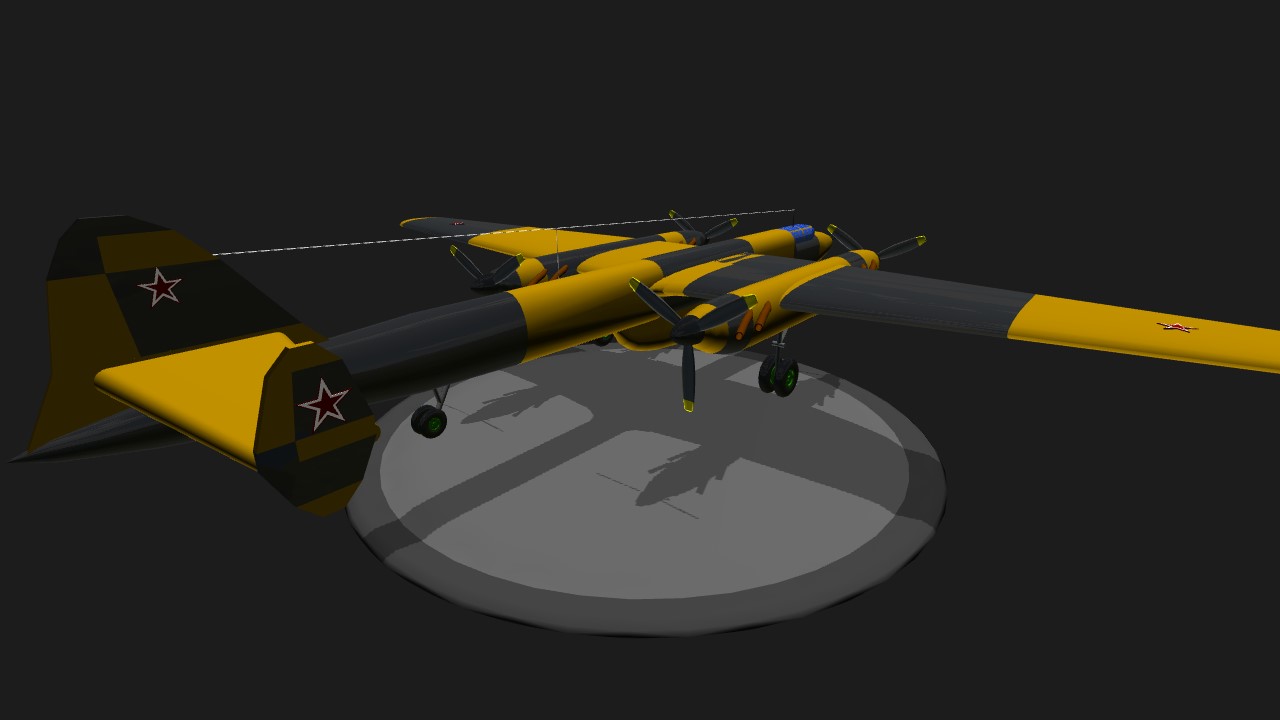
Enough said, time to get down to business. This, so far, is the plane with the most parts on my account. I gave it a desert camouflage ground strike scheme found mostly on Sukhoi Su-17 “Fitter” jets from the late Cold War era. Now of course the main feature of this craft is the massive 100mm V-0902 cannon fitted underneath the fuselage with a total of 15 shells. Besides that, there is a single 23mm NS-23 cannon found in the nose.


Features
- Four liquid-cooled Mikulin AM-43NV 12-cylinder piston engines.
- Custom landing gear
- One 100mm V-0902 cannon - (Original by RussianAS. It can be found here.)
- One 23mm NS-23 cannon (orange tracers)
- Flaps
Controls
- For takeoff (realistically), drop the flaps and increase throttle to about 73%. Once you reach 106 mph (170 km/h), pull back half-way on the stick and it will gracefully go into the air. At this point you can increase the throttle to 100% and pick up your landing gear.
- For landing (without crashing), reduce throttle to about 44% and slow it down to 144 mph (231 km/h) where you should deploy the flaps and increase the throttle to around 60% to reliably keep it above its 106 mph (170 km/h) stall speed. Pitch up gently once you are nearing landing. If you are on the ground by now, you can apply the brakes whenever you want.
History
Although extremely little is know about this airplane, I was able to piece together as much of its history as I could from various sources through persistent research and digging.
IL-14T:
First conceived in 1946, the IL-14T (“T” meaning Tyazhelovooruzhenny, or heavily armed) was proposed as an alternate bomber destroyer/heavy ground attack variant of the B proposal of the IL-14 high-speed medium bomber. If fact, there was an earlier bomber destroyer variant of the IL-14 that retained defensive armament and added two powerful cannons of a smaller caliber. The full armament of that specific aircraft was made up of one 23mm NS-23 and two 45mm NS-45 cannons in the nose, one dorsal 20mm B-20 cannon, and another 20mm B-20 in the ventral position directly below the dorsal position behind the bomb bay.
The IL-14T was slightly modified in order to accept the newly proposed 100mm V-0902; a profoundly heavier and more powerful weapon. The fuselage length was increased, and the defensive armament was removed. Due to the length of the V-0902’s barrel, the retractible nose wheel was modified to retract forwards instead of to the rear, and the retracting tail wheel to protect the rear propeller blades was also kept. Improved engines were also envisioned in the form of the liquid-cooled Mikulin AM-43NV fuel-injected V12 piston engine driving 3 blade propellers.
Even though the idea was brought up in 1946, work on the blueprints was not started until late 1947. Blueprints of the IL-14T were completed in April of 1948, and work on the full-scale mockup was started in July with it being completed in December of 1948. The mockup was tested in the wind tunnel in March and showed to have acceptable aerodynamics, which prompted the decision to go ahead and build a prototype. Unfortunately in June of 1949, the IL-14T, and later, the 100mm V-0902 cannon, were cancelled in favor of new missile technology.
100mm V-0902:
In 1948 in the TsNII-58 works, the design of the 100 mm aviation automatic gun V-0902 was begun. It was supposed to arm bombers like the Tu-2 and Tu-4: naturally, any small fighter, whether piston-engined (Yak-3, La-5, La-7, La-9, etc.) or a jet (Yak-15, MiG-9, etc.), could not physically carry this gun because of its weight and recoil.
The 100 mm V-0902 gun utilized a long-recoil mechanism and had a 15-round magazine. To reduce recoil as much as possible of the host aircraft, it was equipped with a very effective muzzle brake which absorbed up to 65% of the recoil energy. It was also designed to be particularly compact. The weight of the gun without its ammo box was 2,976 lb (1,350 kg), and the rate of fire was 30.5 rounds per minute. The recoil force was 10,000 lb (4,535 kg). The firing and reloading controls would be located in the pilot's cockpit of the host aircraft
In 1948, an experimental V-0902 was made and production tests were carried out. In 1949, stationary tests and firing trials were carried out and the gun was modified accordingly. The experimental gun was prepared for flight tests at the end of the year, but no trace of any documents concerning flight tests has been found.
TsNII-58 developed three shells for the V-0902: OFZT (high-explosive incendiary tracer), BRZT (armor-piercing high-explosive), and a special sub-projectile incendiary shell (Basically a large-caliber shotgun shell with smaller high-explosive incendiary projectiles inside.).
The OFZT round weighed 59.54 lb (27 kg) of explosives and was 990mm long. The propellant charge weighed 9.86 lb (4.47 kg) and provided a muzzle velocity of 2,657 ft/s (810 m/s), with a maximum chamber pressure of 2850 kg/m2. Tests showed that it was effective out to a range of 3,280-3,936 ft (1,000-1,200 m).
The BRZT round had a weight of 59.5 lb (27.34 kg) and length of 956mm. The propellant charge weighed 10.03 lb (4.55 kg), and the muzzle velocity was 800 m/s. The shell used an MD-8 fuze, and the tracer burned for 5 seconds. During tests this shell penetrated 120 mm of armor at a 30° striking angle, at a distance of 1,968 ft (600 m).
For shooting at air targets there was a special shotgun-style shell with small high-explosive incendiary projectiles. The shell weighed 34.4 lb (15.6 kg) and contained 1.33 lb (0.605 kg) of explosives (a burst charge) and 93 high-explosive-incendiary sub-projectiles weighing between 52 and 61 grams. The shell was equipped with a VM-30 time fuze. In 1948-1949 experimental batches of these shells with both formation and ring arrangements of the high-explosive incendiary projectiles were tested. The effectiveness of the shell and ability of the projectiles to ignite aircraft were tested by shooting at aircraft on the ground.
The 100mm V-0902 gun became the most powerful automatic aircraft weapon, not only in the USSR, but also, apparently, in the world. From the technical point of view it was a masterpiece of engineering. The problem was that it was five years too late. In 1944-1945 a high-speed heavy piston-engined fighter with the V-0902 could have safely engaged close formations of B-17 and B-29 bombers from a distance of 1 km or more. But the appearance of jet fighters cardinally changed the tactics of the air battle, and heavy large-caliber cannons lost their value completely.
- Sources: Grabin Aircraft Guns, Secret Projects Forum UK, Airwar.ru
Gallery
Unfortunately, the blueprints of the IL-14T have not been found. Since there is nothing, apart from a small description, as to how the IL-14T would have looked like, these are all the pictures shown that have relevance to the IL-14T
Three-view drawing of IL-14 proposal B

Side-view drawing of the 100mm V-0902 automatic cannon

Specifications
Spotlights
- Trainzo 6.4 years ago
- BlackhattAircraft 6.4 years ago
- Armyguy1534 6.3 years ago
General Characteristics
- Created On iOS
- Wingspan 99.3ft (30.3m)
- Length 87.5ft (26.7m)
- Height 20.2ft (6.2m)
- Empty Weight N/A
- Loaded Weight 31,890lbs (14,465kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 0.422
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.15
- Wing Loading 24.7lbs/ft2 (120.4kg/m2)
- Wing Area 1,293.7ft2 (120.2m2)
- Drag Points 11679
Parts
- Number of Parts 528
- Control Surfaces 16
- Performance Cost 1,934






@AircraftoftheRedStar np
Thank you for spotlight and the upvote!
@Armyguy1534
Thank you! @INF101
Yep
Thank you for the upvotes.
@BlackhattAircraft
@nuclearvodka
@TheFantasticTyphoon
Yes it was reused for the airliner. @TurtlesThatFly
Was this plane's designation given to the airliner il-14? I could not find it anywhere
Thank you.
@SuperSix
@Tonnkatu500
@Trainzo
Cool , great job . Nice plane .
Lol the closest one to that was the T-34-122@JamesBoA
Np @AircraftoftheRedStar
Thank you! @USSR
Thanks! I am literally shaking with excitement over my accomplishment. @JamesBoA
@TitanIncorperated
@TheFantasticTyphoon
@BlackhattAircraft
@thefalkenreich
@aplayer
@SuperSix
@Nerfenthusiast
@USSR