I made it exactly 800 parts 💔🙏😭
Anyways
About Vietnam Airlines
Vietnam Airlines (Vietnamese: Hãng hàng không Quốc gia Việt Nam, Vietnam National Airlines) is the flag carrier of Vietnam. The airline was founded in 1956 and later established as a state-owned enterprise in April 1989. Vietnam Airlines is headquartered in Long Biên district, Hanoi, with hubs at Noi Bai International Airport in Hanoi and Tan Son Nhat International Airport in Ho Chi Minh City. The airline flies 117 routes across 19 countries, excluding codeshared services
Vietnam Airlines B787-9

From its inception until the early 1990s, Vietnam Airlines was a minor carrier within the aviation industry as it was hampered by a variety of factors including the socio-economic and political situation of the country. With the government's normalization of relations with the United States, the airline could expand, improve its products and services, and modernize its ageing fleet. In 1996, the Vietnamese government brought together 20 service companies to form Vietnam Airlines Corporation, with the airline itself as the centrepiece. In 2010, the corporation was restructured into a limited liability company and renamed Vietnam Airlines Company Limited. A seven seat management board, appointed by the Vietnamese Prime Minister, oversees the company.
As passenger transport constitutes its core activity, Vietnam Airlines plays a crucial role in the economic development of the country. It owns 100% of Vietnam Air Service Company, a regional airline in southern Vietnam and almost 99% of the low cost carrier Pacific Airlines. In addition, the corporation earns revenue from airline catering and the maintenance and overhauling of aircraft through a number of its subsidiaries, including Vietnam Airlines Engineering Company and Vietnam Airlines Caterers. The company has also diversified its investments in the aircraft leasing and airport ground-servicing industries, and is looking to manufacture aircraft components. It controls and operates a cargo division, Vietnam Airlines Cargo.
History
Vietnam Airlines has its origins in January 1956, when it was established by the North Vietnamese government under the name Vietnam Civil Aviation (Vietnamese: Hàng không Việt Nam, Vietnam Aviation) following the nationalization of Gia Lam Airport. It was instituted after the government signed Decree No. 666/TTg. Under the designation 919th Transport Air Force Regiment (Trung đoàn Không quân vận tải 919), the airline was created as part of the air force for civilian purposes with support from both the Soviet Union and China; initially, its fleet consisted of two Lisunov Li-2s that were later replaced by two Ilyushin Il-14 and three Aero Ae-45s. This was due to an embargo that prohibited the airline from leasing and/or buying American technology or components.
Ilyushin IL-14 Vietnam Air Force Regiment 919 at the Vietnam Military History Museum
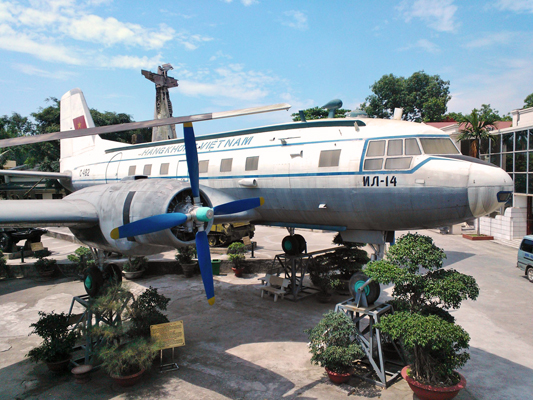

The airline's development and expansion was seriously hampered by the Vietnam War (1955–1975). Following the war, its first international destination was Beijing, followed by Vientiane in 1976. During that year, the airline was known as General Department of Civil Aviation in Vietnam, and began full operations; it carried around 21,000 passengers, one-third of whom were on international flights, and 3,000 tonnes (6,600,000 lb) of cargo. In 1978, another important destination of Vietnam Airlines was added, with flights offered to Bangkok. The late 1980s and early 1990s saw the expansion of the network to Hong Kong, Kuala Lumpur, Manila and Singapore.
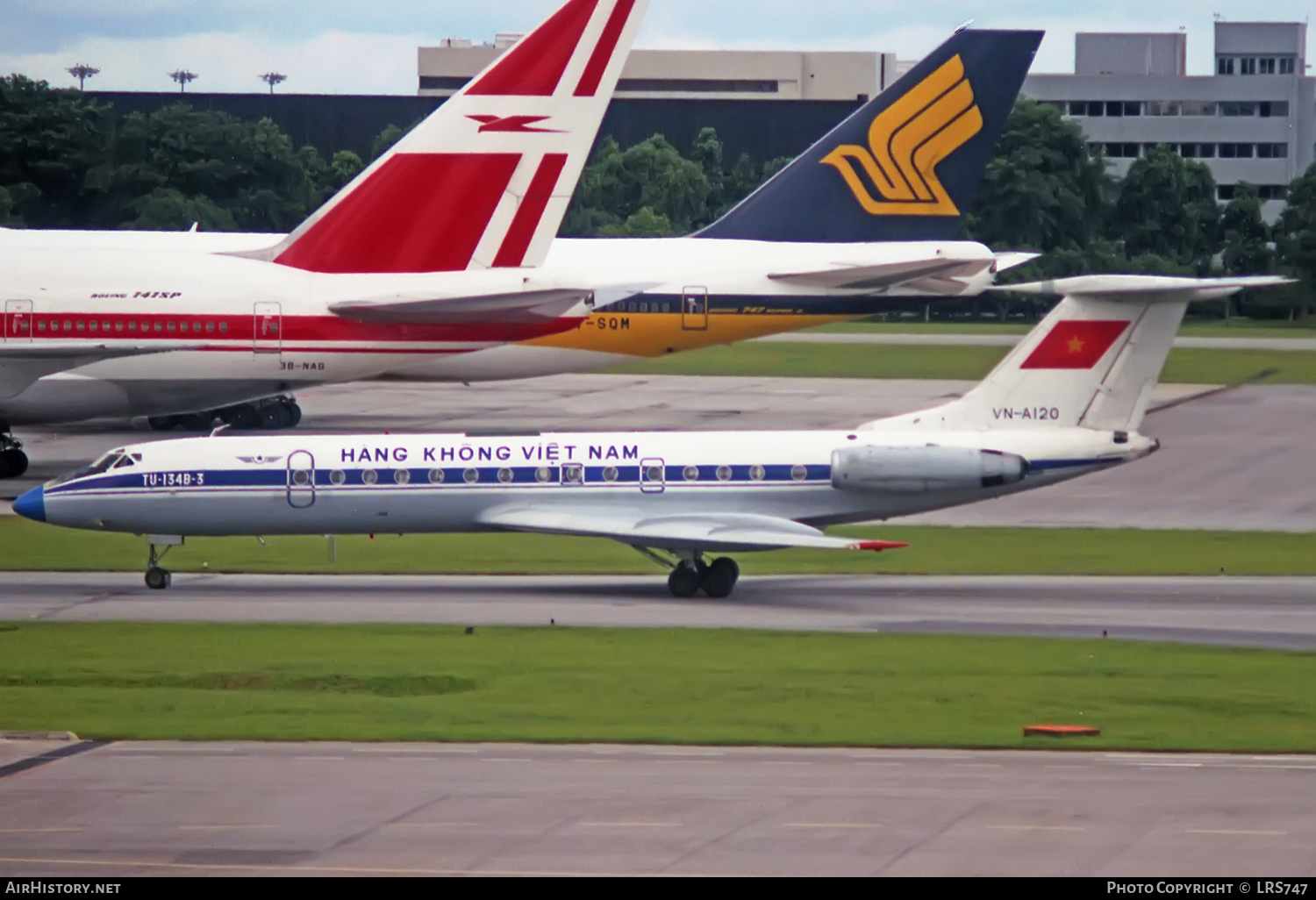
In 1990, the company initiated discussions regarding the incorporation of Western-built aircraft into the fleet. Later that year, however, the carrier had to cancel the acquisition of two Airbus A310s due to their use of US-manufactured engines. By July 1991, the airline struck a wet-lease agreement with Dutch lessor TransAvia. The aircraft involved was a Boeing 737-300, that arrived in Vietnam Airlines' livery. However, the aircraft was returned after the U.S. State Department pressured the Dutch lessor to remove the aircraft from Vietnam. Subsequently, Vietnam Airlines organized a similar but more complicated deal with TEA Basle, who spent the rest of 1991 negotiating a deal with US authorities. Eventually, a solution stating that the Boeing 737 must be positioned outside Vietnam, with no logo or lettering of Vietnam Airlines. On these conditions, it could operate on behalf of Vietnam Airlines was reached. In December 1991, Cathay Pacific and Vietnam Airlines agreed on a 50–50 joint venture to operate between Hong Kong and Vietnam, as the airline's Tupolev Tu-134 fleet did not meet Kai Tak Airport's noise restrictions
New enterprise (1993-2006)
The airline became the flag carrier of Vietnam in 1993, after having completed a restructuring programme that was started four years earlier. In that year, the airline split from the Civil Aviation Administration of Vietnam (CAAV) and became a state enterprise. The move was similar to the reorganization of the Chinese CAAC Airlines into several regional airlines in 1987. Even though the airline gained some independence from the CAAV, it was still known as Civil Aviation Administration of Vietnam within the 1993–1996 period. Also from 1993 to 1995, the 919th Air Force Regiment was eventually re-established as the Flight Crew Division 919 (Đoàn bay 919). The designation that is still being used by the Vietnam Airlines and its personnel until today, marking the carrier's full transformation from a nominal military unit into a wholly civilian and commercial operator.
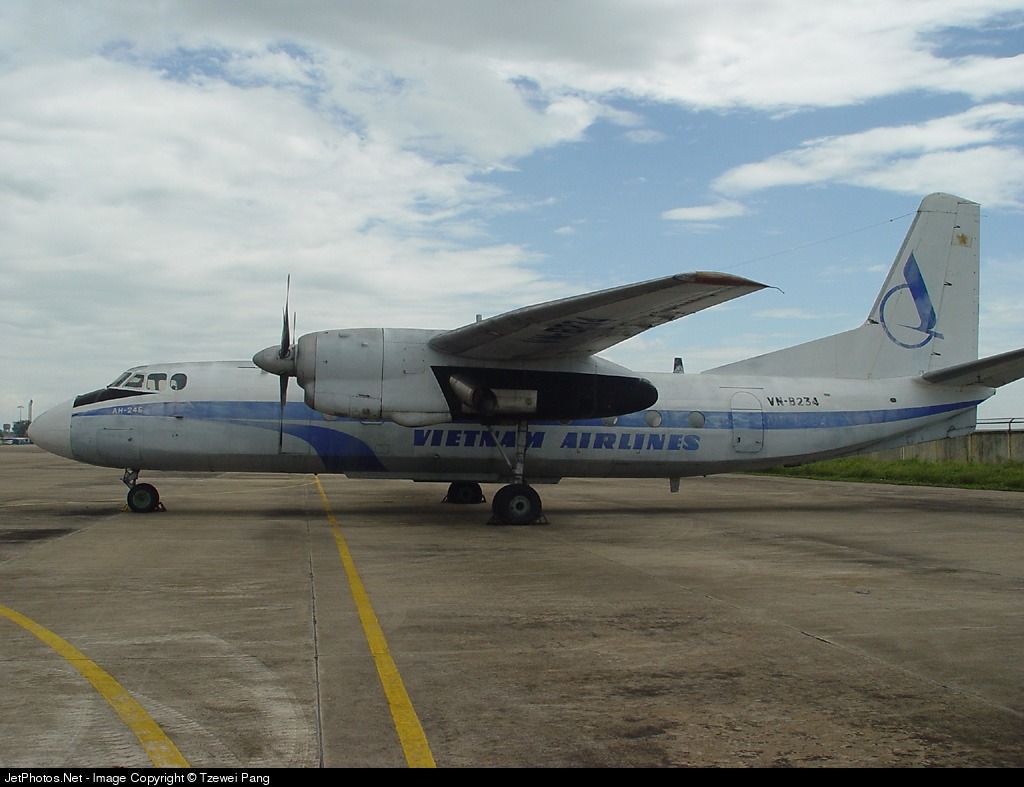
In February 1994, US President Bill Clinton lifted the trade embargo to allow Vietnam Airlines the ability to acquire Western-built aircraft. Consequently, Vietnam Airlines announced in April of the same year that it would be phasing out its inefficient Soviet planes. By April 1995, the fleet consisted of nine Airbus A320s (all of them leased from Air France), 11 Antonov An-24s, four ATR 72s, two Boeing 707-300s, three Ilyushin Il-18s, nine Tupolev Tu-134s and three Yakovlev Yak-40s. At this time the route network comprised 14 domestic destinations (including Ban Me Thuot, Da Nang, Dien Bien Phu, Hue, Nha Trang, Phu Quoc and Pleiku) and 16 international destinations (including Bangkok, Hong Kong, Kuala Lumpur and Singapore). On 27 May 1995, the airline, along with a number of other aviation-related businesses, were incorporated to establish Vietnam Airlines Corporation. Two Fokker 70s were purchased in mid 1995 for US$50 million; they were aimed at partly replacing the Tupolev Tu-134 fleet on domestic routes as well as at serving as VIP transport. In December 1995, discussions with GECAS for the lease of three additional, second-hand Boeing 767-300ERs were under way; these ex-Continental Airlines aircraft would act as a replacement for wet-leased Boeing 767 aircraft (three 300ERs and one 200ER leased from AWAS and Royal Brunei) in the fleet.
Vietnam Airlines An-24 VN-B234

Vietnam Airlines Tu-134 VN-A120 (before it crashed in 1997)

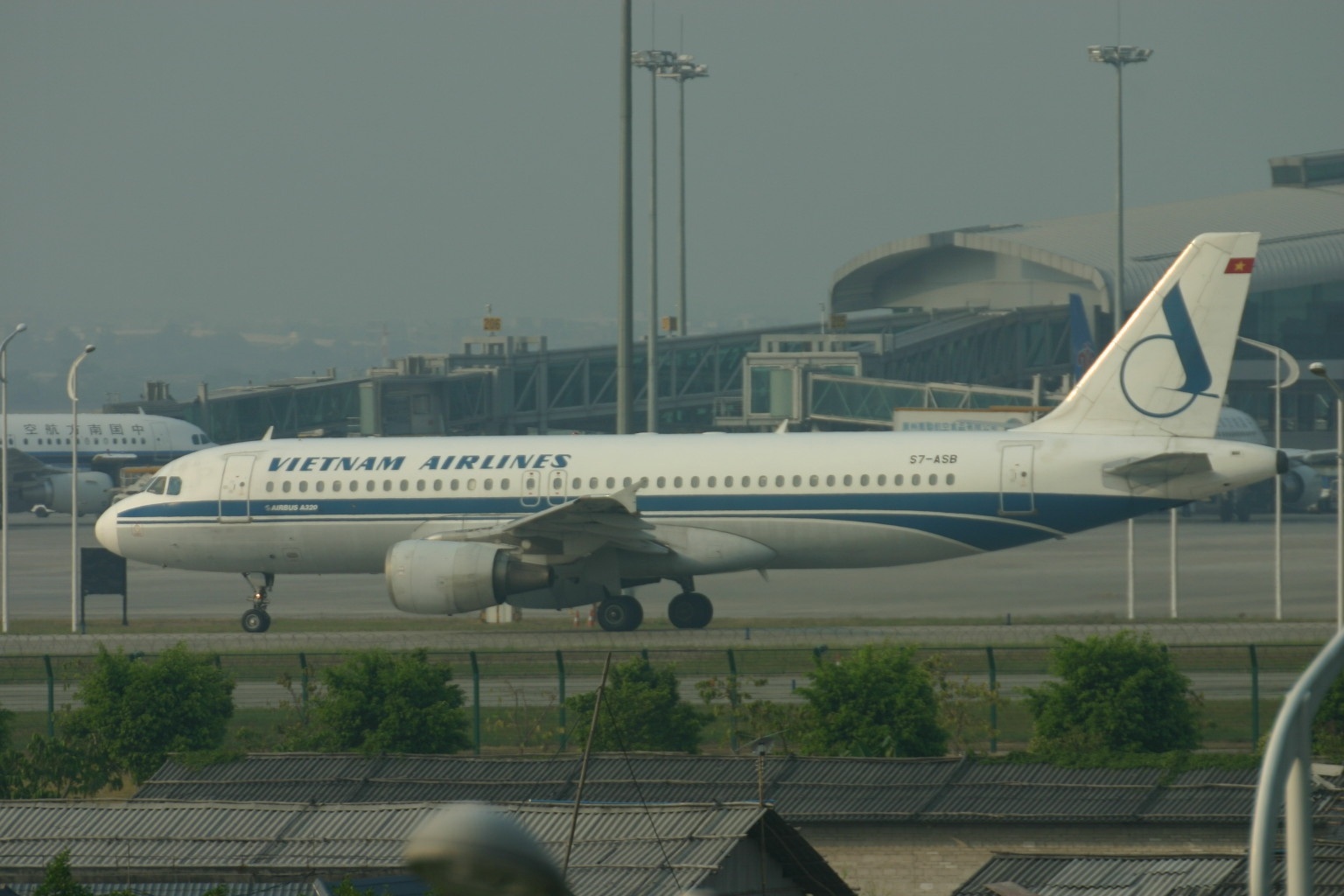
And Vietnam Airlines A320 S7-ASB

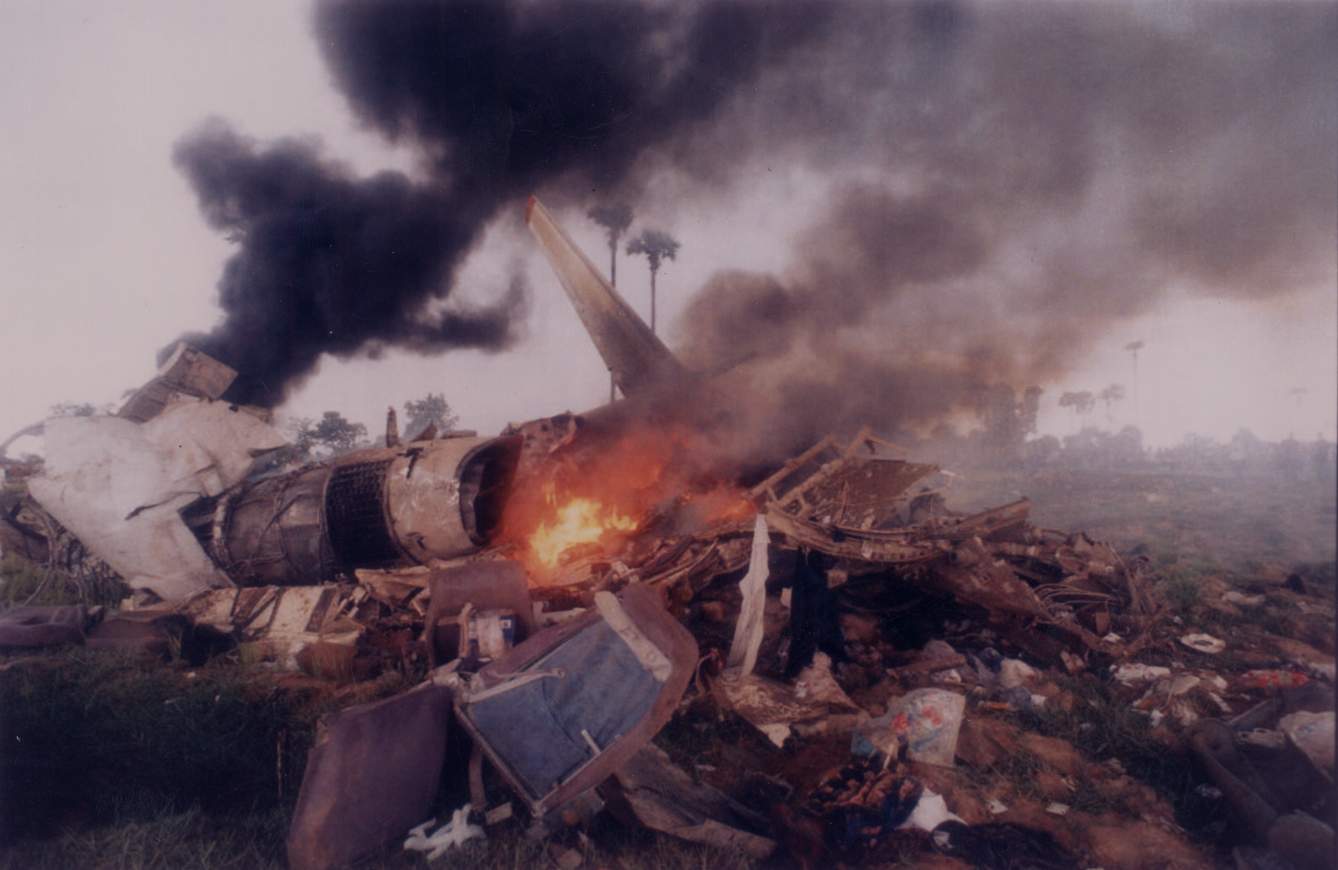
In September 1996, Vietnam Airlines started offering business class services and in 1999, the airline launched its frequent-flyer program, Golden Lotus Plus; During 1996, Vietnam Airlines looked for aircraft which would substitute the A320s wet-leased from Air France when the deal was over. Apart from acquiring further A320s, the airline considered Boeing 737s and McDonnell Douglas MD-90s. In February 1996, GECAS delivered the first of three Boeing 767-300ER to the carrier, on dry-lease for five years. In October the same year, two Boeing 767-300ERs and a Boeing 767-200, on lease from AWAS and Royal Brunei Airlines, respectively, were returned to the lessors, but in early 1997 another Boeing 767-300ER was phased in on a one-year lease from AWAS. With its freedom to operate Western-built aircraft, Vietnam Airlines considered the acquisition of long-haul aircraft to better service Vietnamese living overseas. The Airbus A340, Boeing 747 and the McDonnell Douglas MD-11 were topics of discussion. Meanwhile, two Fokker 70s were acquired in May and July to replace the twelve Tupolev Tu-134s. On 3 September 1997, the crash of a Tupolev Tu-134B, on approach to Phnom Penh's Pochentong Airport in bad weather, resulted in more than 60 fatalities.
Aftermath of Tu-134B Vietnam Airlines 815

Historic agreement with Boeing
In December 2001, Vietnam Airlines signed a historic agreement with Boeing for the acquisition of its first ever US-built aircraft, signalling the start of trade under the Bilateral Trade Agreement between the two countries. The deal involved four Boeing 777-200ERs. The transaction was valued at US$680 million; the first aircraft was initially scheduled for delivery in 2003. These four aircraft, along with six others of the same type that are leased from International Lease Finance Corporation (ILFC), are the flagships of the airline, and serve on medium and long-haul routes, respectively. During that year, the airline carried 3.4 million passengers, 1.9 million of whom were on domestic flights; flights to Beijing resumed and services to Kunming were launched. During 2002, Vietnam Airlines considered a lease offer from Airbus for two Airbus A340-300s, which were never delivered to the airline. On 4 September 2003, a landmark ceremony celebrated the airline's receipt of its first Boeing 777-200ER purchased outright from Boeing. On 28 October, the airline decided to move its operations in Moscow from Sheremetyevo International Airport to Domodedovo International Airport.
Boeing 777-2Q8 Vietnam Airlines VN-A151

About Airbus A300
The Airbus A300 is Airbus' first production aircraft and the world's first twin-engine, wide-body (double-aisle) airliner. It was developed by Airbus Industrie GIE, now merged into Airbus, and manufactured from 1971 to 2007.
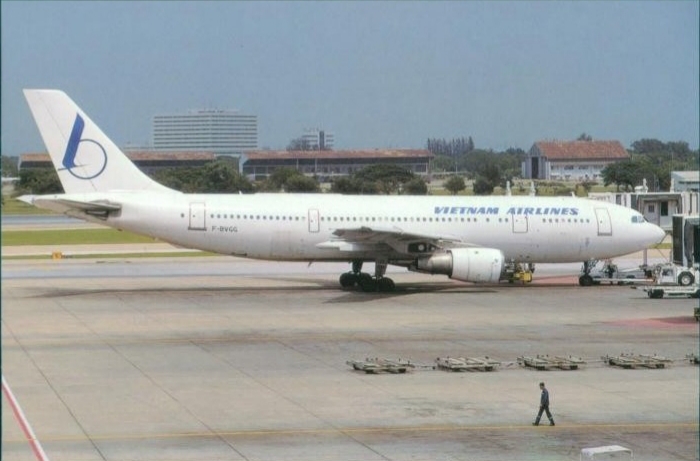
Picture of Vietnam Airlines A300 F-BVGG

In September 1967, aircraft manufacturers in France, West Germany and the United Kingdom signed an initial memorandum of understanding to collaborate to develop an innovative large airliner. The French and West Germans reached a firm agreement on 29 May 1969, after the British withdrew from the project on 10 April 1969. A new collaborative aerospace company, Airbus Industrie GIE, was formally created on 18 December 1970 to develop and produce it. The A300 prototype first flew on 28 October 1972.
The first twin-engine widebody airliner, the A300 typically seats 247 passengers in two classes over a range of 5,375 to 7,500 km (2,900 to 4,050 nmi; 3,340 to 4,660 mi). Initial variants are powered by General Electric CF6-50 or Pratt & Whitney JT9D turbofans and have a three-crew flight deck. The improved A300-600 has a two-crew cockpit and updated CF6-80C2 or PW4000 engines; it made its first flight on 8 July 1983 and entered service later that year. The A300 is the basis of the smaller A310 (first flown in 1982) and was adapted in a freighter version. Its cross section was retained for the larger four-engined A340 (1991) and the larger twin-engined A330 (1992). It is also the basis for the oversize Beluga transport (1994). Unlike most Airbus aircraft, it has a yoke and does not use a fly-by-wire system.
Launch customer Air France introduced the type on 23 May 1974. After limited demand initially, sales took off as the type was proven in early service, beginning three decades of steady orders. It has a similar capacity to the Boeing 767-300, introduced in 1986, but lacked the 767-300ER range. During the 1990s, the A300 became popular with cargo aircraft operators, as both passenger airliner conversions and as original builds. Production ceased in July 2007 after 561 deliveries. As of September 2023, there are 197 A300 family aircraft still in commercial service.
About A300-600
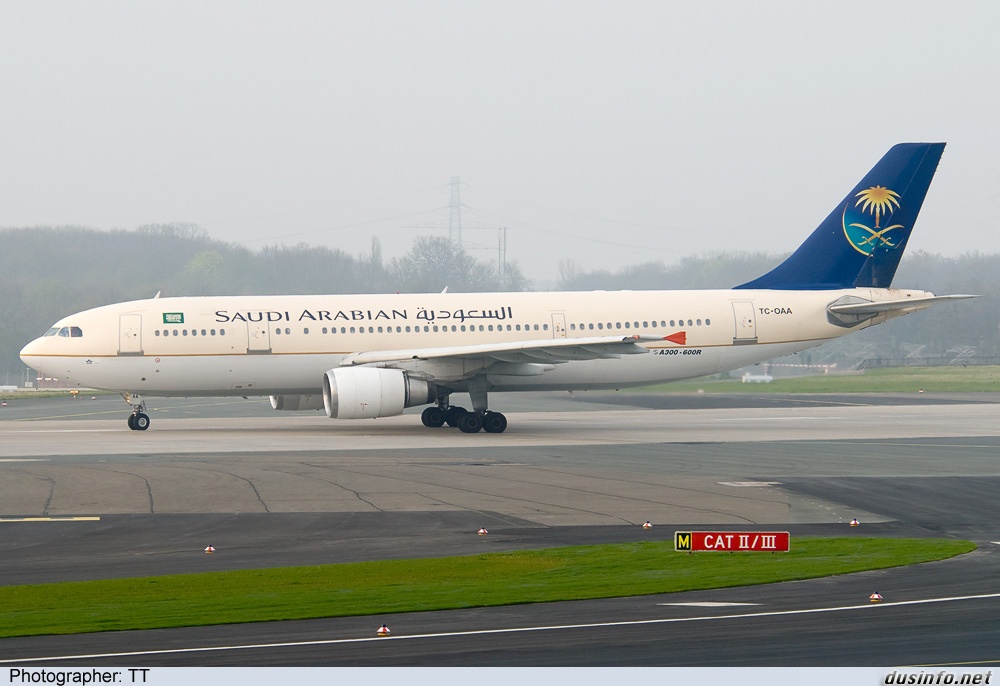
The A300-600, officially designated as the A300B4-600, was slightly longer than the A300B2 and A300B4 variants and had an increased interior space from using a similar rear fuselage to the Airbus A310; this allowed it to have two additional rows of seats. It was initially powered by Pratt & Whitney JT9D-7R4H1 engines, but was later fitted with General Electric CF6-80C2 engines, with Pratt & Whitney PW4156 or PW4158 engines being introduced in 1986. Other changes include an improved wing featuring a recambered trailing edge, the incorporation of simpler single-slotted Fowler flaps, the deletion of slat fences, and the removal of the outboard ailerons after they were deemed unnecessary on the A310. The variant made its first flight on 8 July 1983, was certified on 9 March 1984, and entered service in June 1984 with Saudi Arabian Airlines.
Saudi Arabian Airlines A300-600 TC-OAA (It was now Onur Air)

Specifications
General Characteristics
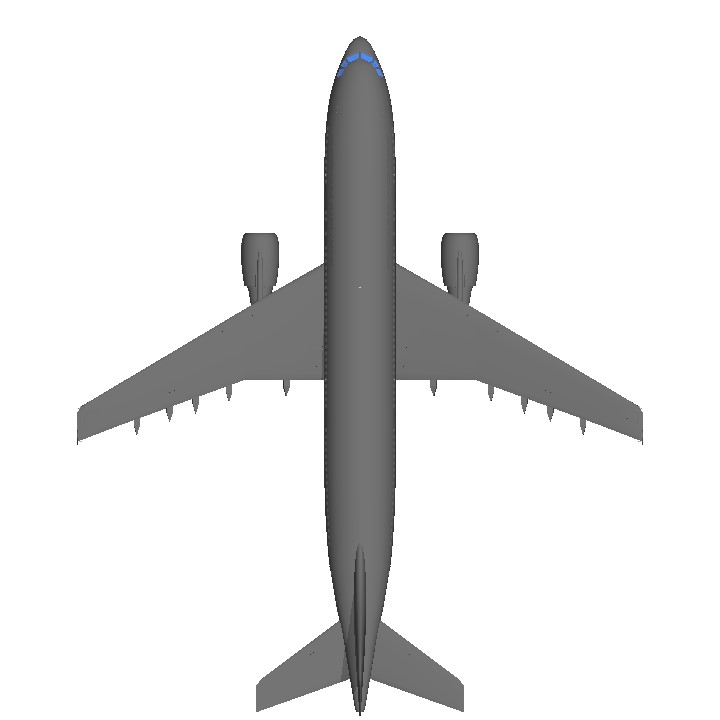
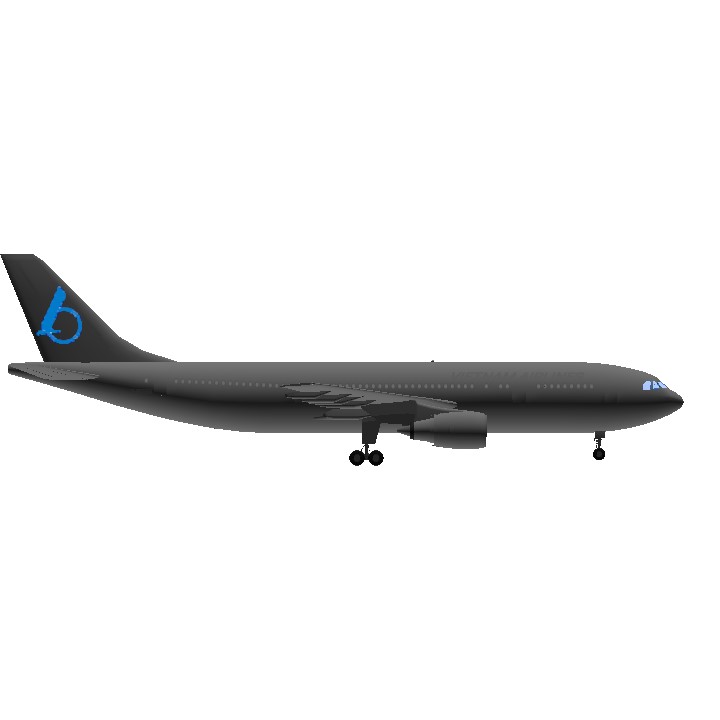
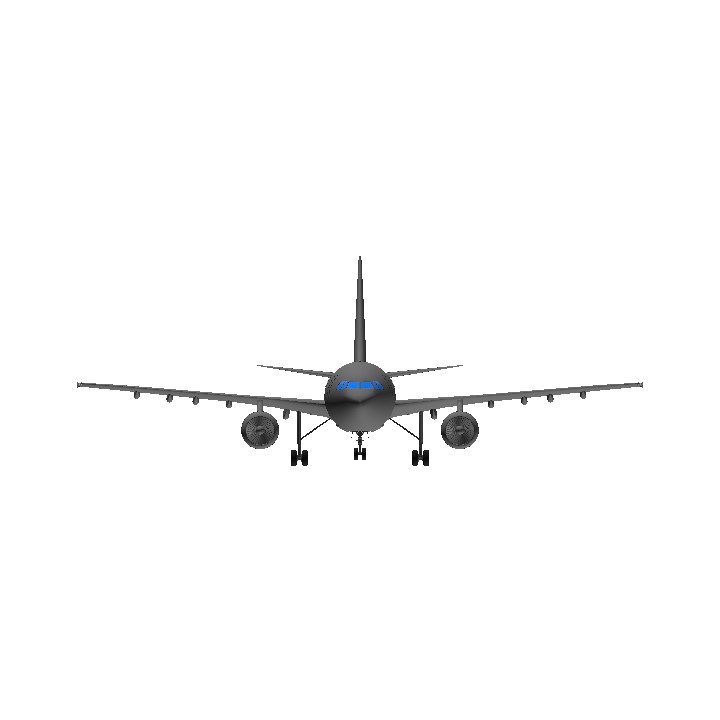
- Predecessor [<800 parts]A300-600[GE]
- Created On Android
- Wingspan 147.1ft (44.8m)
- Length 186.9ft (57.0m)
- Height 54.9ft (16.7m)
- Empty Weight N/A
- Loaded Weight 196,139lbs (88,967kg)
Performance
- Power/Weight Ratio 0.505
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.005
- Wing Loading 61.8lbs/ft2 (301.7kg/m2)
- Wing Area 3,174.0ft2 (294.9m2)
- Drag Points 27175
Parts
- Number of Parts 800
- Control Surfaces 9
- Performance Cost 3,449






first