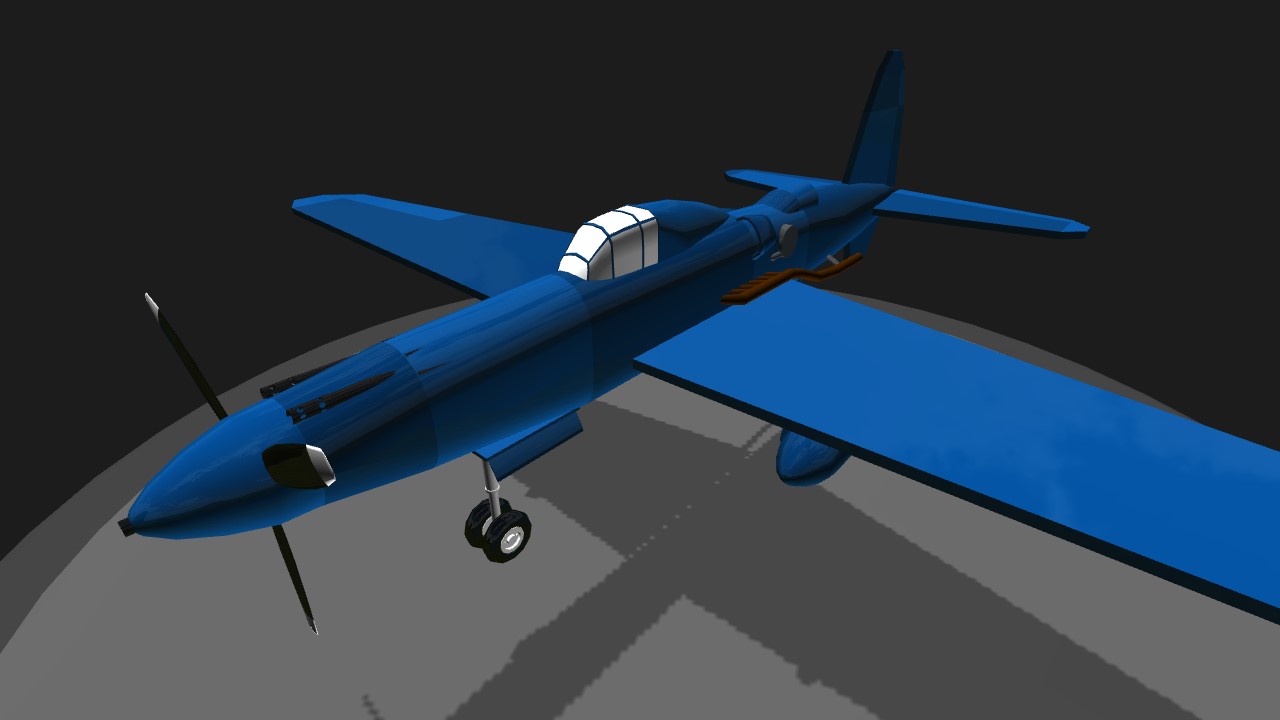
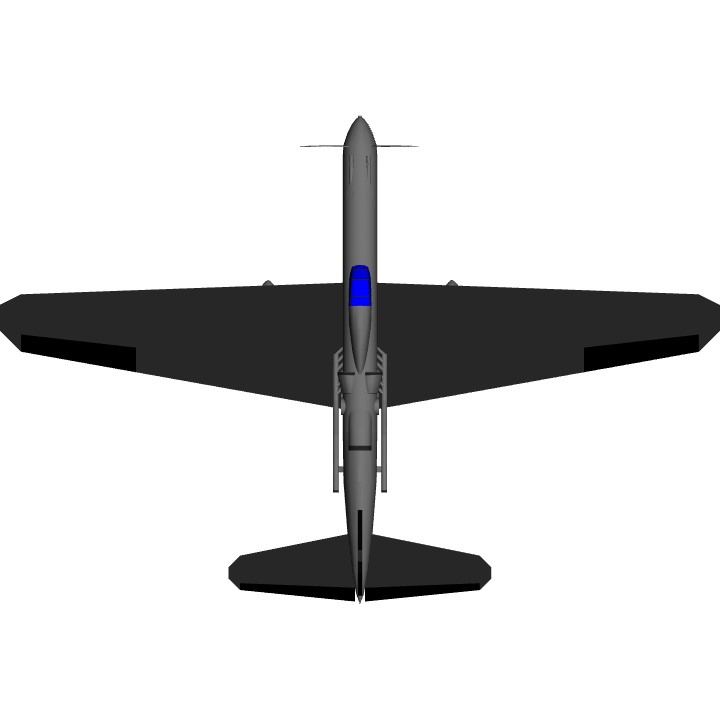
When the year 1939 came around, Sukhoi was looking for a high-speed high-altitude fighter to succeed the Su-1. He came up with a mid-engined design that used the newly developed Klimov M-120TK inline engine with two TK turbo-superchargers. This aircraft is equipped with one 23mm VYa-23 cannon firing through the spinner and two .50 cal UBS machine guns in the upper cowling.
AG-1 - 17 gallon droptanks
History:
In the second half of 1939, P.O. Sukhoi produced a project of a high-speed fighter with the M-120 2TK engine at the Air Force Research Institute. The fighter was intended for conducting active air combat, defeating the enemy with fire in combination with a high flight speed, and "in special conditions of the situation" and for destroying land targets by bombing from a dive. In October 1939, a conclusion was prepared on the draft design, it noted that: "... The design of the aircraft, developed according to the original scheme, is generally rational, because provides a successful layout of the VMG and good flying and tactical characteristics .... The airplane ... has the best aerodynamic shape, not only in comparison with airplanes that have air-cooled engines, but also with airplanes that have liquid-cooled engines due to the possibility of giving a good shape to the front of the fuselage ... "
The conclusions indicated:
"…1. The scheme chosen by the designer in the presence of a powerful motor provides an aircraft with flight data sharply distinguished from the best foreign fighters and fighters of the Air Force of the Red Army, as well as possessing powerful weapons and a good overview ahead. The construction of such an aircraft is extremely necessary.
- Flight-tactical data calculation, in general, are justified and the project as a whole is quite real, and the aircraft of this scheme have already been built and tested in flight. (Bell HR-39, Kolkhoven FK-55) ... ".
The project was approved by the specialists of the Air Force Research Institute, the Conclusion read:
"... Draft design of the cannon high-speed fighter with the engine M-120 and 2TK - to approve.
The main designer to bring the speed of the aircraft to 750 km / h, to make changes to the draft in accordance with this conclusion and the TTT of the Air Force of the Red Army and to show it at the Air Force Research Institute by December 1, 1939.
Put the question before CIAM about the urgent manufacture of the turbocharger to the M-120 engine.
To include the construction of the aircraft in the experimental design for 1940 ".
The draft design was approved by the Chief of the Air Force RKKA Ya.V.Smushkevich on November 4, 1939 with the resolution: "Range increase to 1000 km."
The memorandum to the pilot aircraft construction plan for 1940-41, prepared in mid-December 1939, noted:
"... The pilot aircraft design plan for single-seat high-speed fighters is aimed at obtaining in 1941 experienced fighters with a maximum speed of 750 km / h at an altitude of 9-10 000 m. The present state of high-speed fighters is characterized by the following:
It is being built in the I-16 M-63 series with a maximum speed of 489 km / h.
A series of aircraft I-180 is being prepared, which, with an M-87B at an altitude of 5800, has a speed of 540 km / h.
When installing the M-88, the aircraft should give at an altitude of 7000 m - 580-600 km / h.
The preliminary state testing of the I-28 with M-87B, which at an altitude of 5000 m 545 km / h.
When installing the M-88, the aircraft should give at an altitude of 7000 m - 580-600 km / h.
The fighters with M-105, M-106TK and without TK (with Yakovlev, Sukhoi, Gorbunov, Bisnovat) at the speeds of 620-675 km / h are in construction with the release for testing in February-May 1940.
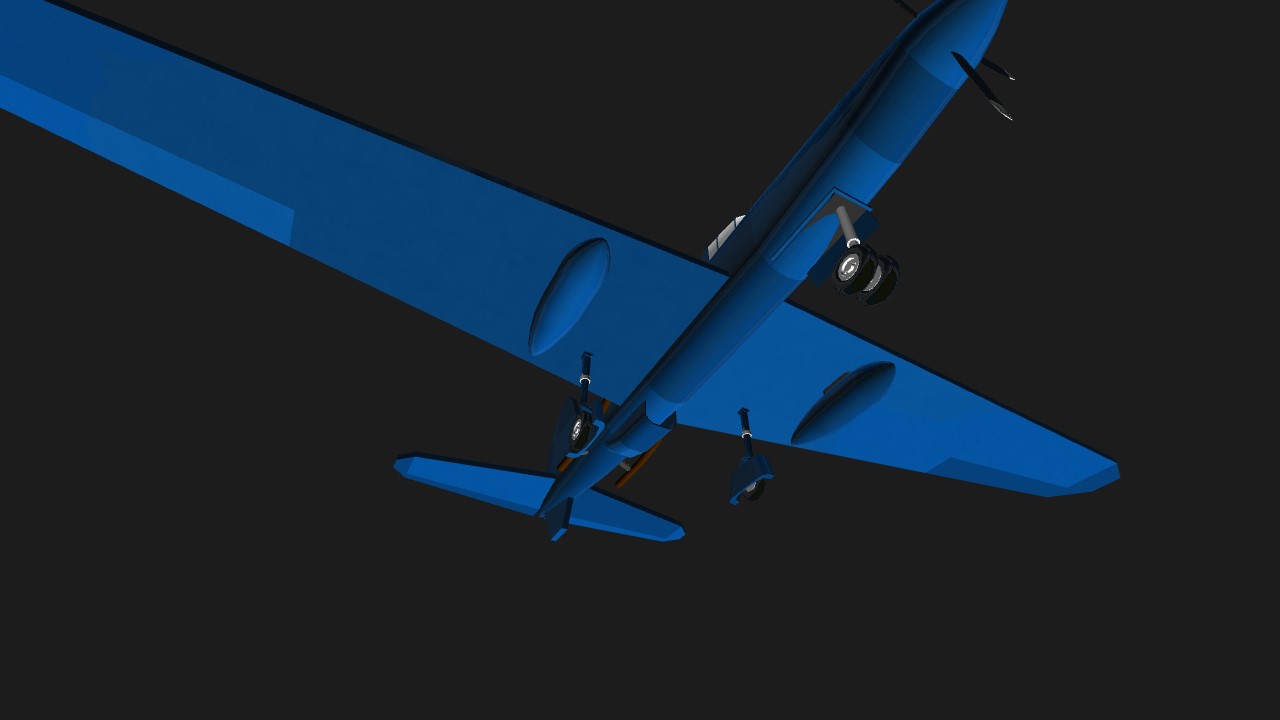
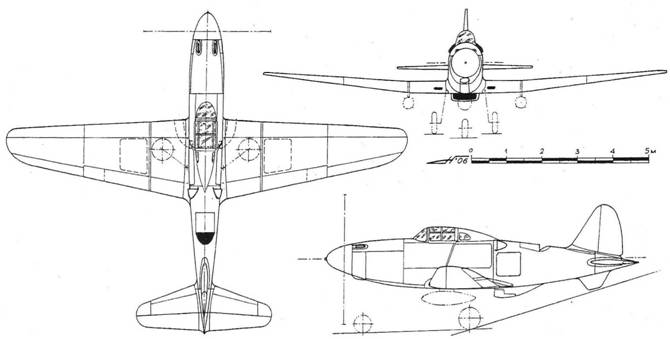
When building a new single-seat fighter with M-120 engines with TK or M-71 with TK, it is possible in 1941 to obtain a maximum speed of 700-725 km / h. Chassis - three-axle with a nose wheel. The front support was retracted along the flow with a slight displacement from the axis of symmetry. The main supports were retracted in a sweep, towards the end parts of the wing. Cleaning and release were carried out using a hydraulic system.
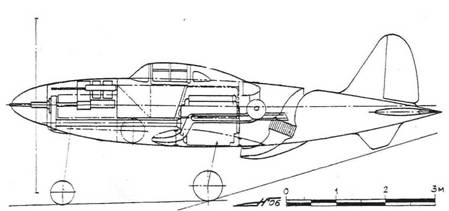
The aircraft was designed for the M-120 liquid-cooled piston engine, installed behind the pilot's back, in the truss fuselage. This arrangement of the engine gave the NPF a well streamlined shape, reducing the moment of inertia and improving the survey of the pilot. Drive propeller VISh-27 was carried out by means of an elongated shaft. The shaft of the chromomagnetic tube was attached to the flange of the motor shaft, passed under the pilot's seat and was connected to the front gearbox via a coupling. The water cooling radiator was located in the HCP behind the motor and was structurally executed in analogy with the Su-1 (Su-3). The M-120 engine, with a claimed power of 1500 hp, was an 18-cylinder assembly of three M-103 engine blocks (one unit up and two down). Turbochargers were located inside the fuselage, on either side of the engine. Exhaust gases from M-120 were brought to the TK, and from them were taken to the channel behind the water radiator. Provision was made for the removal of gases into the channel of the radiator, bypassing the TC. In addition, the exhaust pipes were enclosed in casing, the blowing of which was carried out through the air intakes in the frontal part of the center wing with the outlet of the purge air into the channel behind the water radiator. The intake of exhaust gases and blowing air into the channel behind the water radiator increased the heat content of the gas-air mixture and contributed to the creation of an additional jet thrust. The fuel was placed in two centrifugal protected tanks at 325 kg, to ensure explosion safety, filled with exhaust gases. Suspension of an additional fuel tank for 150 kg was provided. Armament included a 23-mm VYa-23 cannon with ammunition of 100 rounds, firing through the hollow shaft of the reducer and two synchronized UBS machine guns of 12.7 mm caliber (.50 cal), with a total ammunition capacity of 400 rounds.
The aircraft provided for the installation of oxygen and fire fighting equipment, and in the transshipment option - radio stations.
Withdrawal of a fighter with an M-120 engine forced the specialists of the OKB to continue their search for the choice of the shape of a high-speed fighter.
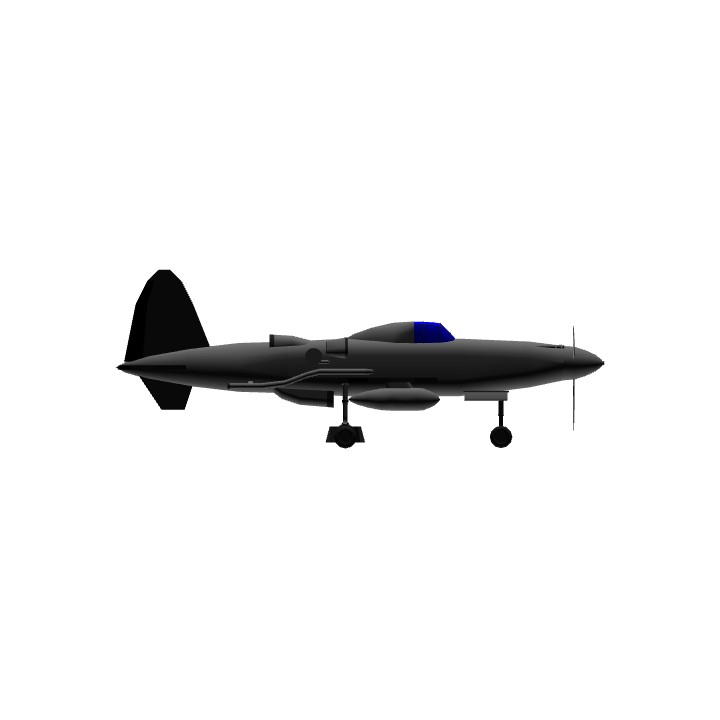
Three-view drawing of I-M-120 (reconstruction)
Inboard profile (reconstruction)
Specifications
General Characteristics
- Created On iOS
- Wingspan 51.4ft (15.7m)
- Length 34.9ft (10.6m)
- Height 12.6ft (3.8m)
- Empty Weight 4,740lbs (2,150kg)
- Loaded Weight 8,445lbs (3,830kg)
Performance
- Horse Power/Weight Ratio 0.165
- Wing Loading 20.5lbs/ft2 (100.2kg/m2)
- Wing Area 411.7ft2 (38.3m2)
- Drag Points 3040
Parts
- Number of Parts 77
- Control Surfaces 6
- Performance Cost 331